In the competitive world of product management, understanding and implementing a customer-centric approach is crucial for success. This comprehensive guide draws insights from top product leaders to help you develop a product mindset that puts the customer at the forefront of every decision. Whether you’re a seasoned product manager or just starting your journey, these strategies will help you create products that truly resonate with your users.
1. Mastering User Research: Getting Inside Your Customer’s Mind
Effective product management starts with a deep understanding of your users. Ben Babcock, User Research Leader at Meta AI, emphasizes the importance of truly knowing your customer. Here are key strategies to enhance your user research:

Regularly Evaluate Team KnowledgeConduct periodic assessments of your team’s customer knowledge. Ask questions like:- Who is our customer?- What do they love or hate about our product?- When was the last time you spoke with a customer?- How are you improving the customer experience?
If team members struggle to answer these questions or haven’t interacted with customers recently, it’s time to refocus on user research.
Bring Customers Into Your OfficeCreate opportunities for direct observation. Consider setting up a customer lab where users can interact with your product in a controlled environment. This firsthand observation can provide invaluable insights into user behavior and pain points.
Utilize Net Promoter Score (NPS)Implement NPS surveys to gauge customer satisfaction. This simple metric asks users how likely they are to recommend your product on a scale of 0–10. Aim for an NPS over 50, which indicates a healthy level of customer satisfaction and loyalty.

2. The Art of Asking the Right Questions: Capturing Authentic Customer Voice
Shoshana Burgett, Owner of Pink Elephant Productions, shares techniques for eliciting genuine customer feedback:
Avoid “Why” QuestionsInstead of asking “why,” which can feel confrontational, use open-ended prompts like “Tell me about your experience” or “Walk me through your process.” This approach encourages users to share more detailed, authentic responses.
Practice Active ListeningAim to listen 80% of the time and speak only 20%. This ratio ensures you’re truly absorbing customer insights rather than leading the conversation.
Examine ExtremesExplore what users love and hate about your product. Understanding these extremes can highlight areas for improvement and features to emphasize.
Ask Probing QuestionsDig deeper with follow-up questions like “What’s most important to you?” or “How often does this happen?” These detailed inquiries can uncover nuanced user needs and preferences.

3. Building an Effective Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
Jori Bell, Director of Product Management at Audible, offers guidance on creating MVPs that truly serve user needs:
Focus on Core User ProblemsIdentify the most pressing user issues and concentrate on solving these first. This approach ensures your MVP addresses critical needs from the outset.
Prioritize High-Impact WorkUse your understanding of user problems to prioritize features that will have the most significant impact. This focus helps create an MVP that delivers real value to users.
Start Small and Iterate QuicklyBegin with the simplest version of your product that still solves the core user problem. Gather feedback early and often, using it to guide rapid iterations and improvements.
Balance Time, Effort, and ValueConstantly evaluate the tradeoffs between development time, effort required, and potential value to users. This ongoing assessment helps maintain focus on the most crucial aspects of your MVP.

4. Designing AI Products That Build Trust
As AI becomes increasingly prevalent in product development, building user trust is paramount. Chris Butler, Product Leader at Google, provides insights on creating trustworthy AI products:
Understand User Mental ModelsRecognize that users’ understanding of AI may differ from reality. Design your product interface and interactions to align with these mental models, making the AI’s role clear and understandable.
Make AI Interpretable and Allow InterventionEnsure users can understand why the AI is making certain decisions. Provide options for users to intervene or override AI decisions when necessary, maintaining a sense of control.
Help Users Avoid ErrorsDesign your AI to guide users away from potential mistakes, but be careful not to remove all sense of agency. Strike a balance between AI assistance and user control.
Define Clear AccountabilityEstablish and communicate who is responsible for AI decisions — the software, the users, or the designers. Clear accountability helps build trust and sets appropriate expectations.

5. The Art of Thoughtful Personalization
Chris Maliwat, Chief Digital Officer at Victoria Beckham Beauty, breaks down the key elements of effective personalization:
Input: Gather Comprehensive User DataCollect both explicit data (user-provided information) and implicit data (behavior patterns, usage history) to create a holistic user profile.
Smarts: Combine AI with Human ExpertiseUse machine learning algorithms to process data, but incorporate domain expertise to ensure personalization efforts align with broader business goals and user needs.
Selection: Curate Based on User Needs and ValuesGo beyond simple product recommendations. Consider user values, preferences, and the context of their interactions with your product when personalizing experiences.
Delivery: Focus on Customer SuccessShift your focus from mere conversion to ensuring customer success with your product. This approach builds long-term loyalty and satisfaction.
6. Creating Habit-Forming Products: Insights from Psychology
Nir Eyal, author of “Hooked,” provides a framework for designing products that become an integral part of users’ routines:
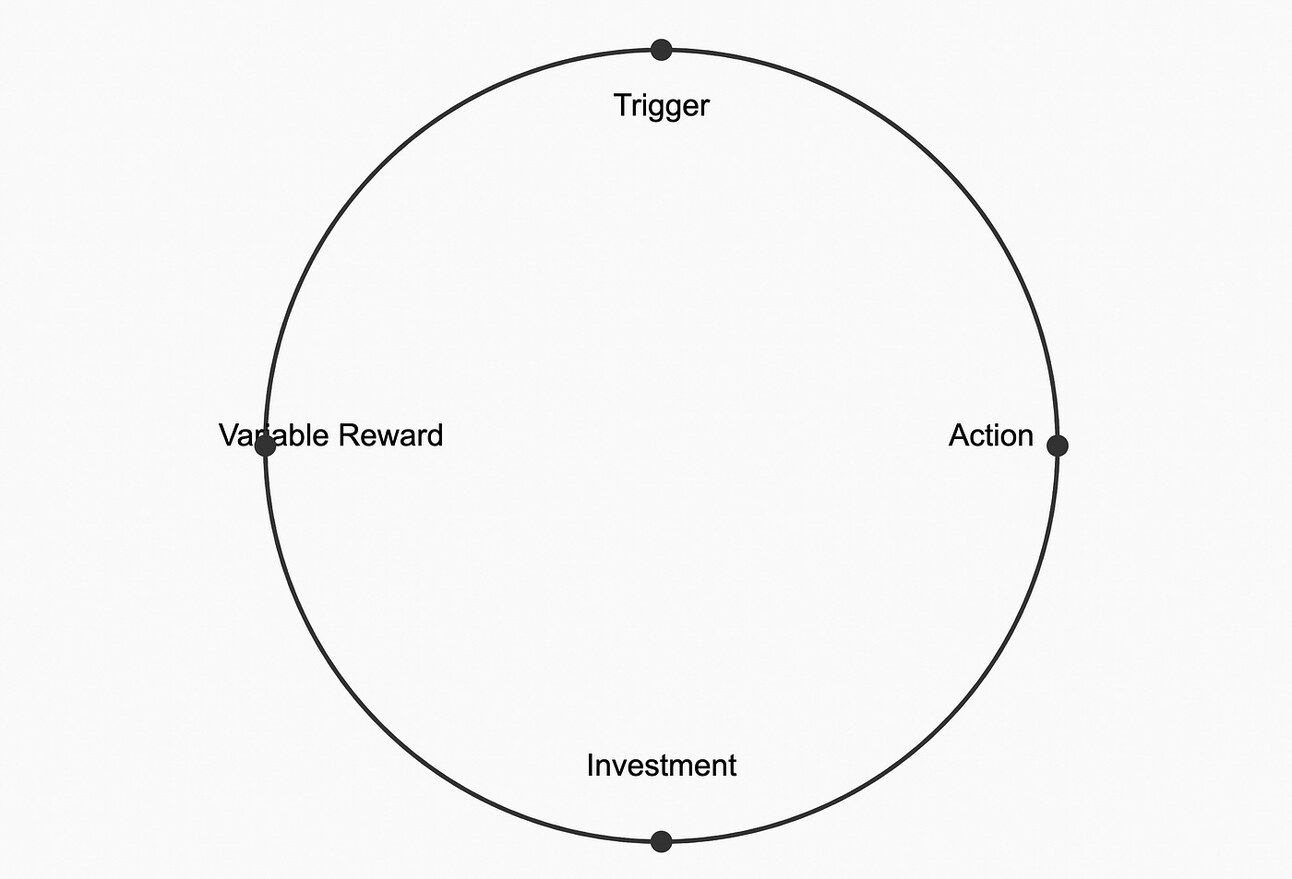
Understand Internal TriggersIdentify the emotional or situational triggers that prompt users to seek out your product. These internal motivators are key to creating habitual use.
Simplify the Core ActionMake the primary action users take with your product as simple and frictionless as possible. The easier it is to use your product, the more likely it is to become a habit.
Provide Variable RewardsIncorporate different types of rewards — tribal (social recognition), hunt (resource acquisition), and self (personal achievement) — to keep users engaged and coming back for more.
Encourage User InvestmentDesign features that allow users to invest time, data, or effort into your product. This investment increases the likelihood of continued use and makes it harder for users to switch to competitors.
Conclusion: Aligning Mission, Customer Needs, and Company Values
Developing a strong product mindset is about more than just understanding techniques — it’s about aligning your mission, your customers’ needs, and your company’s values. As you apply these principles from industry leaders, always strive to create products that not only serve your users but also contribute positively to the world.
Remember, building customer-centric products is an ongoing process. Continuously seek feedback, iterate on your approaches, and stay open to new insights. By maintaining this mindset, you’ll be well-equipped to create products that truly resonate with users and stand out in the competitive product landscape.
I’d love to hear about your experiences in implementing these strategies. What challenges have you faced in adopting a customer-centric approach? What successes have you achieved? Share your thoughts and let’s continue the conversation on building better, more user-focused products.